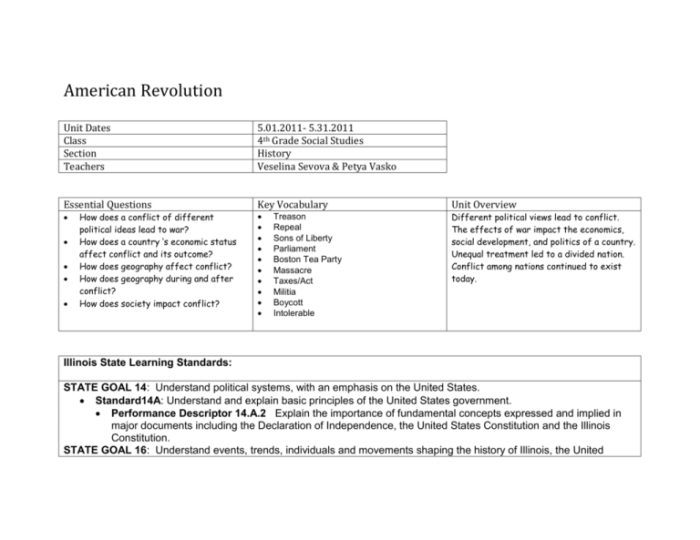
Causes of the american revolution worksheet answer key pdf – Unveiling the Causes of the American Revolution: A Comprehensive Guide through the Worksheet Answer Key PDF, this exploration delves into the pivotal events and grievances that ignited the flames of revolution.
Delving into the depths of British policies, colonial grievances, the influence of Enlightenment ideas, and the escalating events leading to war, this guide unravels the intricate tapestry of factors that culminated in the American Revolution.
British Policies
British policies played a significant role in the growing tensions between Great Britain and its American colonies. These policies aimed to increase revenue and control over the colonies, but they often had the opposite effect, leading to widespread resentment and resistance among colonists.
The Stamp Act
The Stamp Act of 1765 was a tax imposed on all printed materials in the colonies. It was met with widespread opposition from colonists, who argued that it violated their right to taxation without representation.
The Townshend Acts
The Townshend Acts of 1767 imposed new taxes on a range of imported goods. These taxes were also unpopular among colonists, who saw them as an attempt to further assert British authority over the colonies.
The Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was a protest against the Townshend Acts. In 1773, a group of colonists disguised as Native Americans boarded British ships in Boston Harbor and dumped the cargo of tea into the water.
British Economic Policies
In addition to the specific policies mentioned above, British economic policies also contributed to colonial resentment. The British government often granted monopolies to certain companies, which gave them exclusive rights to trade in certain goods. This restricted competition and led to higher prices for colonists.
Colonial Grievances
The British policies described above led to a growing list of grievances among American colonists. These grievances were articulated in a number of documents, including the Declaration of Independence.
Taxation without Representation
One of the most important colonial grievances was the issue of taxation without representation. The colonists argued that they should not be taxed by the British Parliament because they were not represented in that body.
The Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence, adopted by the Continental Congress in 1776, was a formal statement of the colonies’ grievances against Great Britain. It declared that the colonies were independent from Great Britain and that they had the right to govern themselves.
Arguments against British Rule, Causes of the american revolution worksheet answer key pdf
The Declaration of Independence listed a number of arguments against British rule, including:
- The colonists were being taxed without representation.
- The British government was violating the colonists’ natural rights.
- The British government was not providing adequate protection for the colonists.
The Role of Ideas
The American Revolution was influenced by a number of Enlightenment ideas. These ideas emphasized the importance of individual rights, natural law, and the social contract.
Enlightenment Ideas
Enlightenment ideas were spread through the colonies by a number of means, including newspapers, books, and pamphlets. These ideas provided a framework for colonists to understand their grievances against Great Britain and to justify their demand for independence.
Natural Rights and Social Contract Theory
Two of the most important Enlightenment ideas that influenced the American Revolution were natural rights and social contract theory. Natural rights are the rights that all human beings are entitled to simply by virtue of being human. Social contract theory argues that the government is a contract between the people and the government.
If the government violates the contract, the people have the right to overthrow it.
Key Thinkers
Some of the key thinkers who influenced the American Revolution include:
- John Locke
- Jean-Jacques Rousseau
- Thomas Paine
Events Leading to War
The American Revolution did not begin overnight. It was a gradual process that began with the Stamp Act of 1765 and culminated in the Declaration of Independence in 1776.
Timeline of Key Events
- 1765: Stamp Act
- 1767: Townshend Acts
- 1770: Boston Massacre
- 1773: Boston Tea Party
- 1774: First Continental Congress
- 1775: Battle of Lexington and Concord
- 1776: Declaration of Independence
The Boston Massacre and the Battle of Lexington and Concord
The Boston Massacre and the Battle of Lexington and Concord were two of the most important events leading up to the American Revolution. The Boston Massacre occurred in 1770 when British soldiers fired on a crowd of colonists, killing five people.
The Battle of Lexington and Concord occurred in 1775 when British soldiers clashed with colonial militia. These events led to a breakdown in relations between Great Britain and the colonies and helped to push the colonies towards independence.
The Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from the colonies that was held in Philadelphia in 1774 and 1775. The Continental Congress organized colonial resistance to British rule and helped to prepare the colonies for war.
The Declaration of Independence: Causes Of The American Revolution Worksheet Answer Key Pdf
The Declaration of Independence was a formal statement of the colonies’ grievances against Great Britain. It was adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776.
Purpose and Structure
The purpose of the Declaration of Independence was to declare the colonies’ independence from Great Britain and to explain the reasons for that decision. The Declaration is divided into three parts:
- A preamble
- A list of grievances
- A statement of independence
Key Principles and Ideas
The Declaration of Independence expresses a number of key principles and ideas, including:
- All men are created equal.
- All men have certain unalienable rights, including life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
- Governments are instituted to protect the rights of the people.
- If a government becomes destructive of these rights, the people have the right to alter or abolish it.
The War for Independence
The American Revolutionary War was a conflict between Great Britain and the American colonies that lasted from 1775 to 1783. The war ended with the Treaty of Paris, which recognized the independence of the United States.
Major Battles and Campaigns
Some of the major battles and campaigns of the American Revolutionary War include:
- Battle of Saratoga
- Battle of Yorktown
- Saratoga Campaign
- Yorktown Campaign
George Washington and Other Key Figures
George Washington was the commander-in-chief of the Continental Army. Other key figures in the war include:
- Thomas Jefferson
- Benjamin Franklin
- John Adams
Challenges and Obstacles
Both sides faced a number of challenges and obstacles during the war. The Continental Army was often outnumbered and outgunned by the British. The British, on the other hand, had to deal with the challenges of fighting in a foreign land and the logistical difficulties of supplying their troops.
Helpful Answers
What were the primary grievances of American colonists?
American colonists harbored grievances such as taxation without representation, restrictions on trade, and the presence of British troops.
How did Enlightenment ideas contribute to the American Revolution?
Enlightenment ideas, emphasizing natural rights and social contract theory, provided an intellectual framework for colonists to question British authority.
What was the significance of the Declaration of Independence?
The Declaration of Independence formally declared the American colonies’ independence from British rule and Artikeld the principles of self-governance.