Exercise 26 review sheet functional anatomy of the urinary system – Prepare to delve into the intricate world of the urinary system with our comprehensive Exercise 26 Review Sheet. Embark on a journey through the functional anatomy of this vital system, unraveling its remarkable structure and indispensable role in maintaining overall well-being.
This review sheet serves as an invaluable guide, equipping you with a thorough understanding of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Discover the mechanisms of urine production, transport, and storage, while exploring the intricate neural and muscular interplay that governs micturition.
Overview of the Urinary System
The urinary system is a complex network of organs and tissues responsible for maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance, removing waste products from the blood, and regulating blood pressure. It plays a crucial role in overall health and well-being.
Major Organs of the Urinary System
- Kidneys: Filter waste products from the blood and produce urine.
- Ureters: Transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Urinary Bladder: Stores urine until it is released through urination.
- Urethra: Carries urine out of the body.
Functional Anatomy of the Kidneys
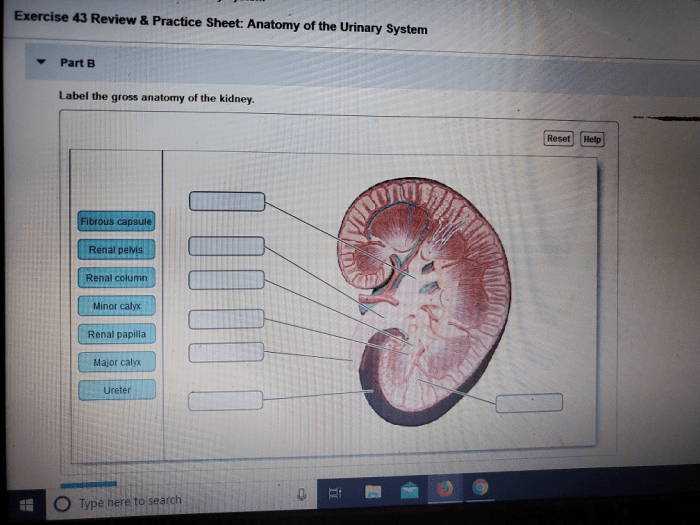
Gross Anatomy
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine. They are composed of an outer cortex and an inner medulla, which is divided into renal pyramids.
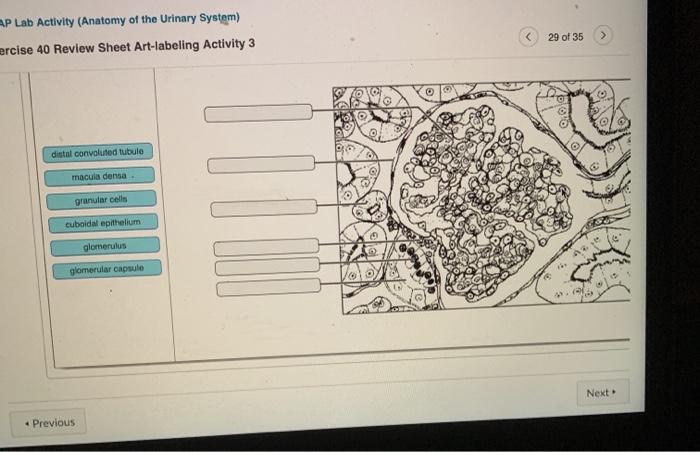
Microscopic Anatomy
The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron, which consists of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle filters waste products from the blood, while the renal tubule reabsorbs essential substances and secretes waste products into the urine.
Blood Supply and Innervation
The kidneys receive blood from the renal arteries and are innervated by the renal nerves, which control blood flow and urine production.
Ureters, Urinary Bladder, and Urethra: Exercise 26 Review Sheet Functional Anatomy Of The Urinary System
Structure and Function of Ureters, Exercise 26 review sheet functional anatomy of the urinary system
The ureters are muscular tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. They are lined with transitional epithelium, which allows them to expand and contract as urine passes through.
Structure and Function of the Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that stores urine until it is released through urination. It is lined with transitional epithelium and has a muscular layer that contracts to expel urine.
Structure and Function of the Urethra
The urethra is a tube that carries urine out of the body. In males, it is also part of the reproductive system and carries semen during ejaculation. In females, it is a shorter tube that opens into the vagina.
Renal Physiology
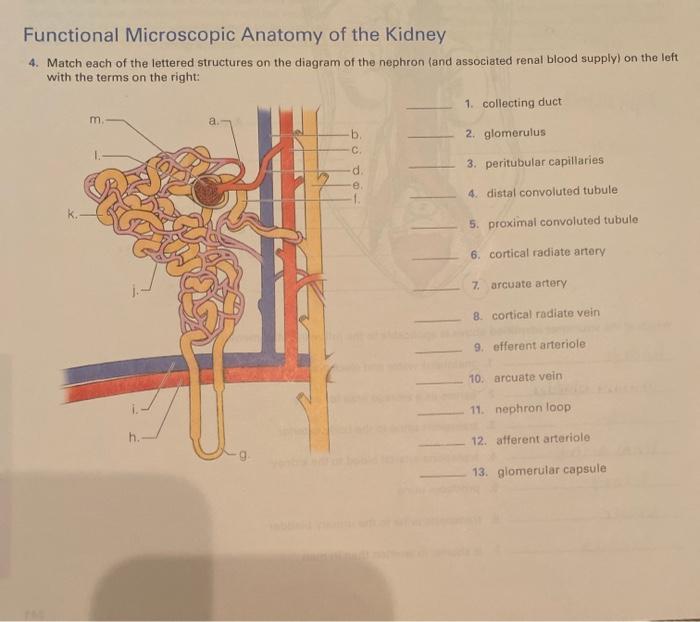
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular filtration is the process by which waste products are filtered from the blood into the renal corpuscle. It occurs due to the high pressure gradient between the glomerular capillaries and the Bowman’s capsule.
Tubular Reabsorption
Tubular reabsorption is the process by which essential substances are reabsorbed from the renal tubule back into the blood. It occurs through active and passive transport mechanisms.
Tubular Secretion
Tubular secretion is the process by which waste products are actively transported from the blood into the renal tubule. It plays a role in the excretion of certain substances, such as creatinine and uric acid.
Hormonal Regulation
The kidneys are regulated by several hormones, including antidiuretic hormone (ADH), aldosterone, and renin. These hormones control fluid and electrolyte balance, as well as blood pressure.
Micturition
Neural and Muscular Mechanisms
Micturition is the process of releasing urine from the urinary bladder. It is controlled by a complex neural and muscular mechanism that involves the detrusor muscle and the external urethral sphincter.
Role of Detrusor Muscle and External Urethral Sphincter
The detrusor muscle contracts to expel urine from the bladder, while the external urethral sphincter relaxes to allow urine to flow out. These muscles are controlled by nerve impulses from the spinal cord and brain.
Factors Affecting Micturition
Micturition can be affected by various factors, including bladder capacity, urine flow rate, and neurological disorders.
Common Urinary System Disorders
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs are bacterial infections that affect any part of the urinary system. They are common in women and can cause symptoms such as pain, burning, and urgency during urination.
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits that form in the kidneys. They can cause pain, nausea, and vomiting, and can lead to urinary tract obstruction if they become large.
Renal Failure
Renal failure is a condition in which the kidneys lose their ability to function properly. It can be caused by a variety of factors, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and certain medications.
Helpful Answers
What are the major organs involved in urine production and excretion?
The kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra are the primary organs responsible for urine production and excretion.
Explain the role of the kidneys in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance.
The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating fluid and electrolyte balance by filtering waste products from the blood, reabsorbing essential substances, and excreting excess fluids and electrolytes in the form of urine.
Describe the mechanisms involved in urine transport and storage.
Urine is transported from the kidneys to the bladder through the ureters, which utilize peristaltic contractions. The bladder stores urine until it reaches a certain volume, triggering the micturition reflex to expel the urine through the urethra.