Lesson 6 becoming familiar with blueprint systems integration – Lesson 6: Becoming Familiar with Blueprint Systems Integration delves into the intricacies of this transformative technology, providing a comprehensive overview of its components, processes, challenges, and future trajectory. This in-depth exploration will equip readers with the knowledge and insights necessary to harness the full potential of blueprint systems integration.
As we delve into this captivating subject, we will uncover the myriad benefits and applications of blueprint systems integration, spanning diverse industries. We will dissect its key components and the collaborative roles they play in achieving seamless integration. Furthermore, we will meticulously examine the step-by-step integration process, highlighting best practices for ensuring a successful implementation.
1. Blueprint Systems Integration Overview
Blueprint systems integration involves combining and coordinating multiple systems, applications, and data sources to create a unified and seamless solution. It enables organizations to streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and gain valuable insights from their data.
Benefits of using blueprint systems integration include:
- Reduced costs through consolidation and optimization
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- Enhanced data visibility and accessibility
- Increased agility and responsiveness to changing business needs
Blueprint systems integration can be applied in various industries, such as:
- Healthcare: Integrating patient records, medical devices, and administrative systems
- Manufacturing: Connecting production equipment, inventory systems, and supply chain management
- Financial services: Combining customer relationship management (CRM) systems, trading platforms, and risk management tools
2. Key Components of Blueprint Systems Integration
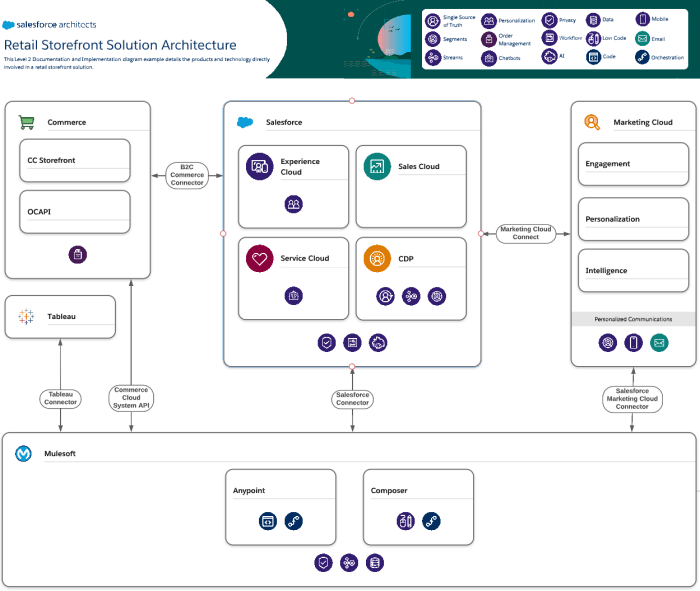
The key components of blueprint systems integration include:
- Enterprise service bus (ESB):Connects and manages communication between different systems
- Data integration platform:Transforms and integrates data from multiple sources
- Application programming interfaces (APIs):Expose functionality and data from one system to other systems
- Integration brokers:Mediate and coordinate interactions between systems
Each component plays a specific role in the integration process:
- ESB: Routes and translates messages between systems
- Data integration platform: Cleanses, transforms, and combines data
- APIs: Provide a standardized way to access data and functionality
- Integration brokers: Manage security, performance, and reliability
These components work together to create a seamless integration that allows systems to communicate, share data, and perform automated tasks.
3. Blueprint Systems Integration Process

The blueprint systems integration process typically involves the following steps:
- Planning:Define the scope, goals, and requirements of the integration
- Design:Create a detailed design for the integration, including system architecture and data mapping
- Development:Implement the integration, including coding, testing, and deployment
- Testing:Validate the integration to ensure it meets the requirements
- Deployment:Release the integration into production
- Maintenance:Monitor and maintain the integration to ensure it continues to meet the business needs
Best practices for ensuring a successful integration include:
- Involve stakeholders throughout the process
- Use a phased approach to minimize risk
- Thoroughly test the integration before deployment
- Continuously monitor and maintain the integration
4. Challenges of Blueprint Systems Integration
Common challenges associated with blueprint systems integration include:
- Complexity:Integrating multiple systems can be complex and time-consuming
- Data quality:Ensuring data accuracy and consistency across different systems
- Security:Maintaining data security and protecting against unauthorized access
- Vendor lock-in:Relying on a single vendor for integration components can limit flexibility
Causes and potential consequences of these challenges:
- Complexity: Can lead to delays, increased costs, and potential errors
- Data quality: Can result in inaccurate or misleading data, affecting decision-making
- Security: Can compromise data integrity and expose sensitive information
- Vendor lock-in: Can limit options for future upgrades or changes
Strategies for overcoming or mitigating these challenges:
- Break down complex integrations into smaller, manageable chunks
- Implement data quality checks and processes
- Prioritize security measures and use industry-standard protocols
- Evaluate multiple vendors and avoid over-reliance on a single provider
5. Future of Blueprint Systems Integration: Lesson 6 Becoming Familiar With Blueprint Systems Integration

Emerging trends and advancements in blueprint systems integration include:
- Cloud computing:Increasing adoption of cloud-based integration platforms
- Artificial intelligence (AI):Using AI to automate integration tasks and improve data analysis
- Low-code/no-code platforms:Making integration more accessible to non-technical users
- Event-driven architecture:Enabling real-time data integration and response
Potential impact of these trends on the future of the industry:
- Increased speed and efficiency of integration projects
- Improved data quality and accuracy
- Lower costs and greater flexibility
- Enhanced business agility and innovation
The future of blueprint systems integration lies in the adoption of innovative technologies and approaches that enable organizations to create seamless and intelligent integrations that drive business value.
FAQ Explained
What is the primary objective of blueprint systems integration?
Blueprint systems integration aims to create a cohesive and seamless flow of data and processes between disparate systems, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and decision-making.
What are the key challenges associated with blueprint systems integration?
Common challenges include data compatibility issues, security concerns, complex system interactions, and the need for skilled professionals to manage the integration process.
How can organizations mitigate the challenges of blueprint systems integration?
Organizations can overcome challenges by conducting thorough planning, establishing clear communication channels, implementing robust security measures, and investing in training and development for their technical teams.